The Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC), India’s ambitious eCommerce transformation project, is widely seen as a retail industry initiative. It promises to decentralize the eCommerce marketplace, leveling the playing field for all sellers, big and small, while also offering localized options for buyers. ONDC aims to raise eCommerce penetration from 8% today to 25% in the next two years. When achieved, this would be a feat unlike anywhere else in the world.
What's important to note is the potential impact of ONDC goes well beyond retail. We believe the next big opportunity will be in the financial services space. For example, ONDC will enable banks to identify and address the needs of micro, small and medium enterprises (MSMEs) by offering working capital loans, CAPEX loans etc. This is a potential growth lever for financial institutions to acquire new customers and grow the share-of-wallet of existing ones.
However, as a developing initiative, banks are still determining how best to start leveraging ONDC. From our experience of working with banks of different sizes and digital maturity, and of understanding the potential of ONDC and other ecosystem-related client projects, we have curated a few of the challenges leaders might face and discuss how to address them.
Opportunities for banks with ONDC
New channels
As a modular and unrestrictive marketplace, the most significant opportunity presented by ONDC is as a new channel for both retail and wholesale use cases. For example, IDFC FIRST, a major Indian bank, is launching a grocery-buying app for its end consumers on the platform. And Yes Bank is using a third-party offering such as SellerApp to provide enhanced access to its MSME clients on ONDC. This approach opens up access to customers who were not able to leverage branches and online channels.
Tech as a service
The combination of buyer and seller apps lets financial services companies becomeholistic banking tech stack providers. This expands the business-to-business-to-customer (B2B2C) landscape, creating additional revenue from subscription or value-added services.
Data-driven banking
For both retail and MSME customers, the wider reach also grants banks access to higher volume and granularity of data about the behaviour of their customers. With every transaction flowing through the bank's payment rails, they have access to customer purchase trends, enabling them to personalize experiences and promote relevant offers and loyalty programs.
For MSME customers especially, data from ONDC-enabled relationships improves visibility into orders and invoices, which can feed into a better assessment of their creditworthiness. As a result, banks can customize financial solutions, leveraging a technology-driven supply chain finance ecosystem.
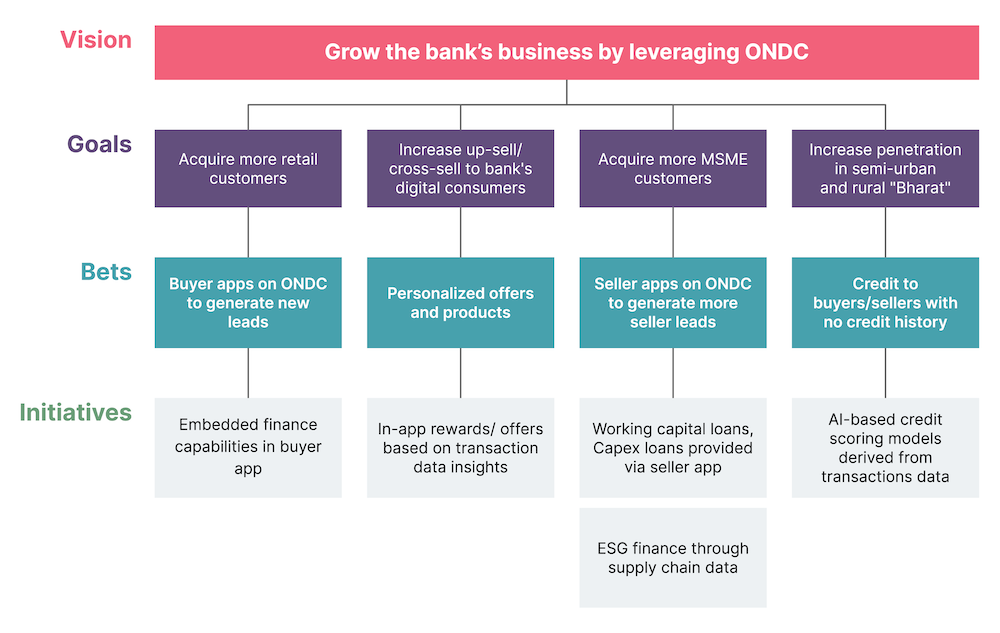
The following diagram shows potential ONDC use cases for banks, envisioned using the Lean Value Tree framework to make the initial experimentation more outcome-oriented.

Challenges for banks with ONDC
Despite its infinite possibilities, ONDC is still an evolving platform, likely to undergo changes and disruptions before stabilizing. Here are some key challenges we foresee banks will face:
Grievance redressal
Grievance redressal mechanisms are critical to maintaining trust-based relationships with customers. But policies around this are still under development by ONDC. While the first instance is expected to be resolved by ONDC, it is not yet clear how follow-ups will be managed. Therefore, financial institutions launching buyer/seller apps need a more robust mechanism for resolving grievances if they want to maintain trust in their brand. They need to have a rigorous risk governance approach and not solely rely on ONDC for the same.
Privacy and data security
Banks will also be responsible for ensuring privacy and data security safeguards. Presently, policies governing ONDC-specific data and country/sector-wide data are awaited. Banks, financial services and insurance players will do well to be proactive and define their own data governance guardrails with ONDC in mind, easing their compliance journey when the policies come into force.
Policies to scale
As the number of participants is not limited on the ONDC platform, all policies need to be defined for scale. It is also vital that these policies evolve with time. So, banks must embrace a principle-based model instead of a rule-based model.
Customer experience benchmarks
To become successful and stay competitive on ONDC, banks must outpace or at least match the UI/UX, tech maturity and fraud management capabilities of existing marketplaces such as Amazon and Flipkart. This would be instrumental in enhancing the confidence of end consumers to switch to ONDC over the long term.
Getting started with ONDC
As we’ve seen, the challenges are as critical and complex as the exciting opportunities that ONDC presents. To overcome these challenges and leverage the new paradigm that ONDC heralds, banks must begin by carefully evaluating their use cases for complexity, effort and exceptions, along with a solid business rationale. They must embrace the platform's evolution and stay agile to evolve with it.
They must forge strategic partnerships with technological allies who can help navigate the extensive taxonomies of leveraging a platform like ONDC. The partner must also have experience with open-source frameworks and related security/scalability aspects.
We were winners of the ONDC Hackathon in 2021 and have been partnering with ONDC for various aspects of solutioning since then.
Disclaimer: The statements and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the positions of Thoughtworks.


















